Asynchronous file sharing allows teams to share, access, and collaborate on files without needing to work simultaneously. However, this flexibility introduces risks like data breaches, unauthorized access, and compliance challenges. To ensure secure file sharing, follow these key practices:
Key Takeaways:
- Encryption: Use AES-256 for storage and TLS 1.3 for transfers. Opt for end-to-end encryption and zero-knowledge architecture for added security.
- Access Controls: Implement role-based permissions, granular settings, and quarterly reviews to limit file access.
- Authentication: Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) and Single Sign-On (SSO) to protect accounts.
- Compliance: Align with GDPR, HIPAA, and other regulations by maintaining audit trails, retention policies, and secure data handling.
- Secure Platforms: Choose tools with integrated security features, external user management, and AI-powered productivity features.
Quick Checklist:
- Encryption: AES-256, TLS 1.3, end-to-end, and secure key management.
- Permissions: Role-based access, granular controls, and regular audits.
- Authentication: MFA, SSO, and adaptive security measures.
- Compliance: Privacy policies, data retention, and regulatory adherence.
- Collaboration Tools: Unified platforms with seamless integrations and secure AI tools.
By following these steps, you can protect sensitive data while enabling efficient, secure collaboration across time zones.
Encryption Standards and Secure Transfers
Strong encryption plays a critical role in keeping files safe during storage and transfer, helping to prevent breaches and ensuring compliance with security regulations.
File Encryption Best Practices
AES-256 encryption is widely regarded as the top choice for safeguarding files at rest. With its 256-bit keys, AES-256 offers strong protection against unauthorized access. In fact, the U.S. government mandates its use for classified data, and leading cloud providers like Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure rely on it as their default encryption method.
When files are stored, AES-256 ensures that even if someone gains unauthorized access to the servers, the data remains unreadable. This is especially important in asynchronous environments where file access may happen at varying times.
For securing files during transfer, TLS 1.3 encryption is the standard. TLS 1.3 enhances both speed and security by removing outdated cryptographic algorithms that could be vulnerable to attacks. Together, AES-256 for storage and TLS 1.3 for transfers create a robust, end-to-end security framework.
Another essential layer of protection is end-to-end encryption. This method ensures that only the sender and the intended recipient can decrypt the files, keeping even the service provider from accessing the content. For organizations managing sensitive material, such as screen recordings of proprietary software or confidential presentations, end-to-end encryption is a must.
To further strengthen security, implementing a zero-knowledge architecture is key. This means encryption and decryption happen on the user’s device, ensuring that the service provider never sees unencrypted data. This approach minimizes risks from internal breaches or surveillance requests.
The next step in a strong encryption strategy is effective key management.
Key Management and Security
Even with advanced encryption, the security of encrypted data depends heavily on how encryption keys are managed. Without proper key management, even the strongest encryption can be compromised.
Regularly rotating encryption keys – such as every 90 days for high-security environments – limits the damage if a key is exposed. Automated key rotation systems can handle this process seamlessly, ensuring security without disrupting workflows.
Secure key storage is another critical component. Hardware security modules (HSMs) or dedicated key management services are ideal for storing encryption keys separately from the encrypted data. This separation makes it far more difficult for attackers to access both the data and the keys. Cloud-based solutions like AWS Key Management Service or Azure Key Vault offer enterprise-grade security while reducing the need for organizations to maintain their own HSM infrastructure.
To balance security with accessibility, organizations can implement key escrow policies. These policies allow authorized personnel to recover encrypted files if employees lose access or leave the company. However, strict access controls and detailed audit trails are necessary to prevent misuse of escrowed keys.
Regular audit verification of key management systems is essential. Quarterly audits, at a minimum, can track key access, rotation schedules, and any unauthorized attempts to access keys. For industries subject to regulations like SOX or HIPAA, maintaining detailed logs of key management activities is crucial for compliance.
Using multi-layer key protection further reduces risks. For instance, separate encryption keys can be assigned to different types of content – one set for screen recordings and another for financial documents. This segmentation limits the impact of potential breaches and simplifies implementing role-based access controls.
Additionally, key management systems should support geographic restrictions to ensure that encryption keys for sensitive data remain within approved jurisdictions. This feature is especially important for multinational organizations that need to comply with data sovereignty laws in various countries.
Access Controls and Permissions
Access controls are the backbone of secure file sharing. They ensure that only authorized individuals can access specific files at appropriate times. Without proper management of permissions, even the most advanced encryption becomes useless if sensitive files fall into the wrong hands.
Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC)
Role-based access controls make managing security simpler by assigning permissions based on job roles rather than individual users. This system reduces the administrative workload while maintaining strong security practices throughout your organization.
Start by defining clear role hierarchies. For instance:
- Executives might need access to all strategic files.
- Project managers may only need access to project-related documents.
- Marketing teams could be limited to campaign materials.
It’s crucial to enforce the principle of least privilege, granting users only the access they need to perform their roles. For example, content creators might have editing rights for marketing videos but no ability to delete project folders.
Regularly review these roles. A quarterly audit can help ensure permissions align with any changes in responsibilities or team structures.
Adding a separation of duties provides an extra layer of security. This means splitting critical tasks between multiple people. For example, one person might upload financial reports, while another is responsible for approving their distribution. This reduces the risk of any one individual having unchecked control over sensitive processes.
Granular file permissions can further refine and enhance access control.
File Permission Settings
Granular permissions allow you to control how users interact with files, offering options like view-only, edit, download, and share. Here’s how these permissions can be applied effectively:
- View-only: Restrict users to simply viewing sensitive files, such as financial reports, without making changes.
- Edit: Allow modifications while using version control to prevent conflicts or accidental overwrites.
- Download: Restrict downloading to prevent data leakage, especially for proprietary or confidential content.
- Share: Limit sharing capabilities to designated managers, incorporating approval workflows for added oversight.
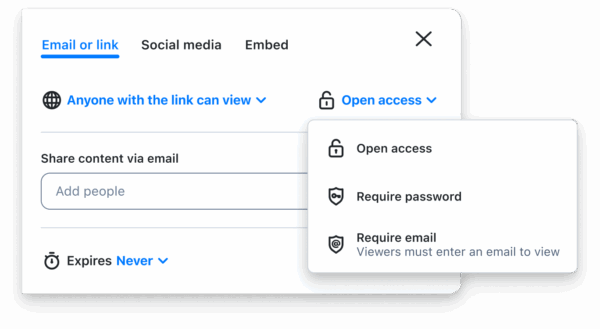
To enhance accountability, features like watermarking and tracking can be used. Watermarks identify recipients when files are viewed or downloaded, while access logs record when and where files are accessed. These tools create a transparent audit trail, which is invaluable for compliance and security investigations.
Simplify permission management with permission inheritance. This feature automatically applies folder-level settings to newly added files. For example, when a team uploads files to a project folder, those files inherit the folder’s permissions, eliminating the need for manual configuration.
When working with external collaborators, additional controls are necessary.
External User Management
Managing access for external users – such as clients, vendors, or partners – requires extra precautions, as these individuals operate outside your organization’s direct oversight.
Use guest accounts with restricted permissions and domain-based sharing rules to limit external access. Guest accounts typically have tightly controlled permissions, limited file access, and automatic expiration dates. Domain restrictions ensure files are only shared with approved email domains.
Monitoring external users is critical when sensitive data is involved. Track their interactions with shared files, including viewing times, download attempts, and sharing activities. If unusual patterns emerge, such as excessive downloads or access from unexpected locations, it could signal a compromised account or unauthorized distribution.
Geographic controls can also enhance security by restricting file access based on location. For example, if compliance rules require that data remain within specific countries, geographic restrictions ensure that shared files stay within approved regions.
Finally, conduct regular external access reviews to identify and remove outdated permissions. Monthly audits can reveal expired projects, completed contracts, or changing business relationships where access is no longer needed. Promptly revoking unnecessary permissions reduces your organization’s exposure to potential security risks.
Authentication and Identity Verification
Strong authentication is the cornerstone of protecting shared files from unauthorized access. Without it, sensitive systems and data are left exposed. Modern approaches to authentication use multiple layers of verification to ensure that only authorized users can gain access.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through two or more factors. This method significantly reduces risks, even if passwords are stolen through phishing or data breaches.
MFA typically combines a password with additional steps like a device token or biometric verification. Time-based one-time passwords (TOTP), generated by apps like Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator, serve as a reliable second factor. These codes refresh every 30 seconds, adding a dynamic layer of protection.
For even stronger security, hardware security keys stand out. Unlike SMS-based methods, which can be compromised through SIM swapping, hardware keys provide phishing-resistant authentication.
Adaptive authentication takes things further by analyzing user behavior and risk factors. For instance, if a marketing manager who usually logs in from New York during regular business hours suddenly tries to access files from London at 3:00 AM, the system might prompt for extra verification steps.
To prevent lockouts, backup authentication methods – like offline codes or alternative apps – are essential. Push notifications via authenticator apps also improve user experience by offering a smoother process compared to SMS codes. These notifications often include details like location, device type, and timestamp, helping users make informed decisions to approve or deny access attempts.
MFA sets the groundwork for a unified security approach. When paired with Single Sign-On (SSO), it creates a seamless and robust authentication framework.
Single Sign-On (SSO) Integration
Single Sign-On simplifies authentication by allowing users to access multiple systems and applications with just one set of credentials. This reduces the hassle of managing multiple passwords, centralizes security, and helps with compliance tracking. When combined with MFA, SSO strengthens the overall security structure.
Modern SSO solutions typically use SAML 2.0 and OAuth 2.0 protocols. SAML works well in enterprise environments with established identity providers like Active Directory, while OAuth is ideal for cloud-native systems and API integrations. Both protocols enable detailed attribute sharing, allowing file-sharing platforms to receive critical user information, such as roles, departments, and security clearance levels, directly from the identity provider.
Identity providers like Okta, Azure Active Directory, and Google Workspace offer SSO capabilities with advanced security features. These platforms streamline user management with automated provisioning and deprovisioning while providing detailed audit logs to monitor authentication activities across connected systems.
With just-in-time provisioning, user accounts are automatically created the first time employees access file-sharing platforms via SSO. This eliminates the need for manual account creation and ensures permissions align with organizational roles. When employees change roles or leave the company, centralized deprovisioning quickly revokes access across all systems.
Session management is another key aspect of SSO. Organizations can define how long users remain authenticated. Shorter session timeouts enhance security but may disrupt workflows, while longer sessions improve usability but increase the risk of misuse. Many companies strike a balance with sliding session windows, which extend during active use but expire quickly when idle.
Conditional access policies within SSO add an extra layer of control. These policies can enforce requirements like MFA for accessing sensitive files, block access from unmanaged devices, or restrict file downloads on public networks. Such measures ensure security scales with the sensitivity of the files being accessed.
Modern file-sharing platforms integrate seamlessly with productivity tools when they support these authentication standards. This means users can access shared files directly from tools like Microsoft Office, Slack, or project management apps without repeatedly logging in, reducing friction while maintaining centralized security policies.
Platforms like Zight support SSO integration, allowing organizations to apply consistent authentication standards across their workflows. Whether it’s screen recordings, screenshots, or shared guides, these assets are protected with the same level of security as other critical business content.
Compliance and Privacy Requirements
Compliance isn’t just about following rules, it builds trust and safeguards your reputation. Different industries face unique regulatory demands, and understanding these is key to choosing the right file-sharing solution for your needs.
Data Protection Regulations
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) applies to any organization handling data from EU residents, no matter where the business is based. This regulation requires explicit consent for data processing, allows individuals to access their data, and mandates reporting data breaches within 72 hours. For file sharing, this means using strong encryption, maintaining audit logs, and being ready to locate and delete specific user data upon request.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) governs healthcare organizations and their partners in the U.S. When sharing patient records or medical files, you need platforms with Business Associate Agreements (BAAs), end-to-end encryption, and detailed audit trails. HIPAA also requires safeguards for electronic protected health information (ePHI), including tracking who accessed files and when.
CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) gives California residents control over their personal information. It includes the right to know what data is collected, to delete personal data, and to opt out of data sales. File-sharing platforms must provide clear privacy notices and the ability to quickly locate and delete user data.
SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act) applies to publicly traded companies, enforcing strict controls over financial data. File-sharing systems need to maintain unchangeable audit logs, prevent unauthorized changes to financial documents, and ensure proper segregation of duties. Approval workflows for accessing sensitive financial files are often a requirement.
Other regulations also bring specific demands. PCI DSS requires secure file storage and transmission for credit card data, adhering to strict encryption standards. FERPA mandates educational institutions sharing student records to implement strong access controls and consent protocols. These rules highlight the need for robust security features in your file-sharing platform.
Privacy Policies and Security Audits
A transparent privacy policy is essential. Look for platforms that clearly explain how they handle your data, including retention periods, data processing locations, and responses to government requests.
Third-party security audits are an important trust signal. For example, SOC 2 Type II audits evaluate how platforms manage security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy over a 6-12 month period. These audits verify whether platforms stick to their security commitments.
ISO 27001 certification confirms that a platform has a comprehensive information security management system. This certification requires regular audits and recertification every three years, ensuring continuous security improvements.
Penetration testing reports reveal how platforms respond to simulated attacks. While detailed assessments might not be public, platforms should confirm regular testing schedules and share summaries of their security practices.
Transparency goes beyond certifications. Look for platforms that provide detailed security documentation, regular updates, and clear incident response plans. Platforms should also publish security advisories when vulnerabilities are identified and fixed, showing their commitment to protecting your data.
When evaluating platforms like Zight, check their privacy policies for details on data handling, retention, and user rights. Strong compliance programs often include comprehensive documentation and quick responses to industry-specific regulatory questions. These measures ensure files remain secure, even during asynchronous collaboration.
Remote Wipe and Data Retention Policies
Remote wipe and retention policies add another layer of security to file sharing. Remote wipe is particularly useful if devices are lost, stolen, or if employees leave the company. This feature lets administrators instantly remove sensitive files or revoke access to shared content, preventing unauthorized access.
Remote wipe tools offer precise control. You can delete business files while keeping personal data intact, restrict access to specific shared files, or disable user accounts across all devices. This minimizes disruption while maintaining security.
Data retention policies determine how long files are kept and when they are permanently deleted. Different regulations require varying retention periods – SOX, for instance, may require financial records to be kept for seven years, while GDPR allows individuals to request data deletion at any time. File-sharing platforms should support automated retention schedules that align with these rules.
Legal holds are another important feature. They pause deletion schedules during litigation or investigations, ensuring relevant documents remain intact. Platforms should provide clear audit trails showing when these holds are applied and lifted.
Backup and recovery procedures work alongside retention policies to ensure compliance, even during system failures. However, backups can complicate GDPR deletion requests, as data must also be removed from backup systems within a reasonable timeframe.
Geographic data residency requirements dictate where files can be stored and processed. Some regulations mandate that data stays within specific countries or regions. File-sharing platforms should clearly identify storage locations and offer options for geographic restrictions when needed.
To simplify compliance, consider automated policy enforcement. Platforms can automatically apply retention schedules based on file types, user roles, or content categories, ensuring consistent adherence to regulations without constant administrative oversight.
Secure Collaboration Tools
When it comes to secure asynchronous file sharing, having integrated collaboration tools is key. They ensure consistent access controls and maintain auditability, blending security with productivity to keep workflows smooth and efficient.
All-in-One Platforms for Collaboration
Using a single, unified platform can close the security gaps that often arise when juggling multiple disconnected tools. Think about it: instead of using one service for file sharing, another for screen recording, and yet another for feedback management, an all-in-one solution applies the same security policies across all features. This keeps everything streamlined and safe.
Take Zight as an example. It combines secure file sharing with features like screen recording, screenshot capture, and step-by-step guide creation. What’s great about platforms like this is that they treat every type of content, whether it’s a sensitive financial document or a quick screen recording, with the same level of protection.
Another benefit? Custom branding. By ensuring content is consistently presented in a controlled, branded environment, these platforms help team members recognize legitimate communications. This reduces the risk of falling for phishing attempts that mimic external platforms.
And let’s not forget multi-platform support. Whether your team is working from a desktop, tablet, or smartphone, these platforms ensure the same level of security. This is particularly important for asynchronous collaboration, where people might access shared content from different devices and locations throughout the day.
Integration with Productivity Tools
Integrated tools don’t just make workflows smoother – they also enhance security. Native integrations with platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Jira create seamless and secure bridges between your tools. This way, you don’t have to compromise on security for the sake of convenience.

For instance, when a file is shared through Zight and discussed in Slack, all access logs and security settings remain intact. Plus, the conversation history adds valuable context, which can be crucial for meeting compliance requirements. This kind of centralized audit trail ensures that you know exactly who accessed what and when.
Single Sign-On (SSO) is another game-changer. It simplifies access across connected tools, reducing the need for multiple passwords while keeping security strong. It’s also incredibly useful for administrators – when someone leaves the team or changes roles, access can be revoked across all platforms in one go.
And then there’s workflow automation. Imagine sharing a screen recording in Microsoft Teams and having the platform automatically apply the right access controls based on the channel’s privacy settings or the content’s classification. It’s security on autopilot.
AI-Powered Features for Efficiency
Building on these integrations, AI-powered features take things to the next level by boosting both efficiency and security. Tools like automated transcription, summaries, and translations adhere to the same strict access controls as the original content, ensuring no security corners are cut.
Automated transcription is a lifesaver for asynchronous teams. It lets team members quickly review recorded meetings or training sessions, no matter their time zone. And because the transcription process follows the same security protocols as the original file, there’s no risk of data slipping through the cracks.
AI-powered translations make it easier for international teams to collaborate while keeping data secure. Whether your organization is subject to GDPR or other regulations, you can rest assured that translation processes won’t compromise personal data protection.
Smart summaries are another handy feature. They help team members quickly identify key points in lengthy documents or recordings without exposing the entire content. Of course, users still need the right permissions to access the full content, but summaries let them decide relevance before making a request.
Even the analytics capabilities of these AI tools contribute to security. By tracking which files are most accessed, shared, or referenced, administrators can focus on protecting high-value information. They can also spot unusual behavior, like unexpected sharing patterns, that might signal a security issue.
Best of all, these AI features operate within the same secure environment as your file storage. Any AI-generated content inherits the security classifications and access controls of the original material. This means you can enjoy productivity boosts without sacrificing data protection.
Final Checklist Summary
Key Points for Secure File Sharing
When it comes to secure asynchronous file sharing, a solid framework is essential to protect your data at every stage. This starts with strong encryption standards, both for data at rest and in transit, paired with reliable key management practices that ensure only authorized individuals can access sensitive information.
Access controls and permissions are critical for maintaining security. Role-based access controls (RBAC) help define who can access specific files, while granular permission settings allow you to fine-tune access to individual documents and folders. For external users, stricter controls are necessary to prevent any unauthorized access.
Authentication and identity verification add another layer of protection. Using multi-factor authentication (MFA) can significantly reduce the risk of account breaches, while Single Sign-On (SSO) simplifies access management without compromising security.
Meeting compliance and privacy standards is a non-negotiable aspect of secure file sharing. Whether you’re navigating GDPR, HIPAA, or other regulations, your practices must align with these requirements. This includes setting up data retention policies, enabling remote wipe options for lost devices, and performing regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
Using a unified collaboration platform can streamline your security efforts. All-in-one platforms like Zight ensure consistent security policies across features like file sharing and screen recording. Built-in AI tools for transcription, summaries, and translations can improve productivity while adhering to the same security protocols as your original content.
Refer to the checklist below to confirm your security measures are in place.
Complete Security Checklist
Encryption and Data Protection:
- Use AES-256 encryption for files at rest
- Apply TLS 1.3 or higher for data in transit
- Establish secure key management processes
- Enable automatic encryption for all shared files
Access Controls:
- Set up role-based access controls (RBAC)
- Configure detailed file permissions
- Implement separate policies for external users
- Review and update access permissions quarterly
Authentication:
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all accounts
- Integrate Single Sign-On (SSO) where applicable
- Enforce strong password policies
- Monitor login activity for unusual patterns
Compliance and Governance:
- Identify and adhere to relevant data protection regulations
- Develop and maintain clear privacy policies
- Set up data retention and deletion schedules
- Enable remote wipe for lost or stolen devices
- Conduct regular security audits
Platform and Integration:
- Use platforms with consistent security across all features
- Verify secure integrations with productivity tools
- Ensure AI tools maintain the security of original content
- Regularly test backup and recovery systems
Monitoring and Maintenance:
- Configure automated security alerts
- Track file access and sharing behaviors
- Review user permissions monthly
- Update security policies in response to regulatory changes
- Train your team on best security practices
This checklist serves as a practical guide for maintaining secure file sharing practices. Regular reviews will help ensure your measures remain effective and up to date.
FAQs
What’s the difference between end-to-end encryption and zero-knowledge architecture, and how do they improve file security?
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) works by encrypting files on the sender’s side so that only the intended recipient can decrypt and access them. This process ensures that no one else – not even the service provider – can see the content while it’s in transit or storage. It’s a simple yet powerful way to keep your data private.
Zero-knowledge architecture takes this a step further. With this system, the service provider doesn’t store or have access to your decryption keys, meaning they can’t view or decrypt your files even if they wanted to. This setup reduces reliance on the provider’s security measures and offers an extra layer of protection against breaches or unauthorized access.
Together, these methods provide a strong shield for your files, maintaining privacy and protecting sensitive information when sharing asynchronously.
What steps can organizations take to ensure only authorized users have access to sensitive files?
To keep sensitive files safe and accessible only to the right people, organizations should use role-based access control (RBAC). This system assigns permissions based on specific roles, ensuring that users only access the files they need for their job duties.
For added protection, combine RBAC with multi-factor authentication, encryption, and routine access log audits. These steps not only help block unauthorized access but also support compliance with security policies while safeguarding critical data.
How can companies ensure they comply with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA when sharing files asynchronously?
Companies handling asynchronous file sharing must adhere to regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, making security and data protection non-negotiable priorities. Start by using encryption to protect data both at rest and during transfer. Strengthen this with access controls, such as role-based permissions and multi-factor authentication, to ensure only authorized personnel can access sensitive information. Employ secure file transfer protocols, like SFTP, to further safeguard data.
For HIPAA compliance, signing Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) with service providers is a must. Maintaining detailed audit logs and establishing thorough data protection policies are also key steps to meeting the standards of both GDPR and HIPAA. Regularly reviewing and updating these measures helps maintain compliance and ensures robust security over time.